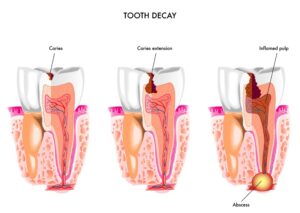
Oral health is closely linked to overall health, and maintaining good oral hygiene contributes to overall well-being. The mouth is a gateway to the body, and poor oral health can have systemic effects on various aspects of health. Here are some key connections between oral health and overall health:
Cardiovascular Health:
Some studies suggest a link between gum disease (periodontitis) and an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. The exact nature of this relationship is still under investigation.
Diabetes:
Diabetes can affect oral health, and conversely, poor oral health may make it more challenging to control blood sugar levels. People with diabetes are at a higher risk of gum disease.
Respiratory Health:
Bacteria in the mouth can be aspirated into the lungs, potentially leading to respiratory infections, pneumonia, or exacerbating existing respiratory conditions.
Pregnancy and Birth:
Periodontal disease has been associated with premature birth and low birth weight. Pregnant women should pay special attention to their oral health.
Arthritis:
Some studies suggest a possible link between gum disease and rheumatoid arthritis. The inflammation in one area of the body may exacerbate inflammation in another.
Dementia:
Poor oral health, particularly gum disease, has been associated with a higher risk of cognitive decline and conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
Kidney Disease:
Chronic kidney disease and periodontitis may be connected, though more research is needed to establish the nature of this relationship.
Digestive Health:
Digestive issues may arise from the swallowing of bacteria from the mouth into the digestive tract.
To maintain good oral health and promote overall well-being:
Brush and floss regularly: Proper oral hygiene practices, including brushing at least twice a day and flossing daily, help prevent the buildup of plaque and bacteria.
Regular dental check-ups: Routine dental visits are essential for professional cleanings, early detection of oral issues, and preventive care.
Healthy lifestyle choices: A nutritious diet, limited sugar intake, and avoidance of tobacco and excessive alcohol contribute to both oral and overall health.
Manage stress: Chronic stress can impact oral health. Stress management techniques can be beneficial.
It’s important to recognize the interplay between oral health and overall health and to address any oral health issues promptly. Regular communication with both dental and medical healthcare providers is crucial for maintaining optimal health across the board.