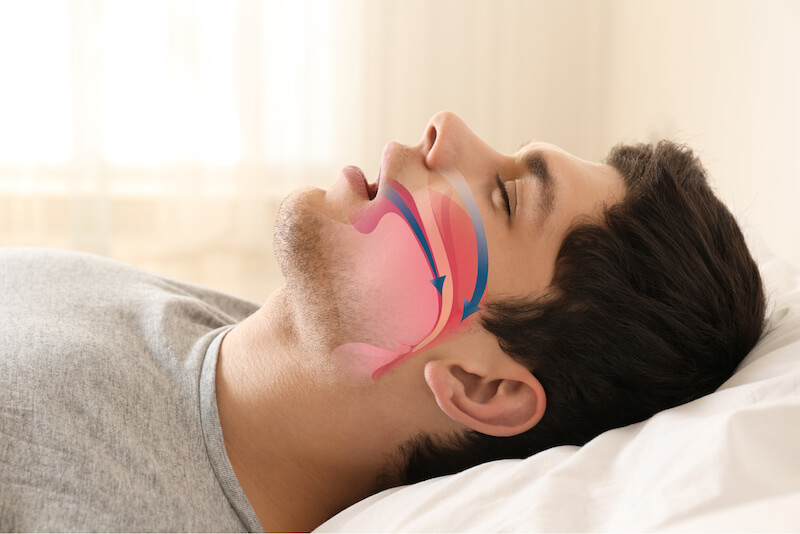
Mouth breathing can significantly impact dental health. Here are some key dental issues associated with habitual mouth breathing:
1. Dry Mouth (Xerostomia) Reduced Saliva Production: Mouth breathing reduces saliva flow, which is crucial for maintaining oral health. Saliva helps neutralize acids, wash away food particles, and control bacteria in the mouth.
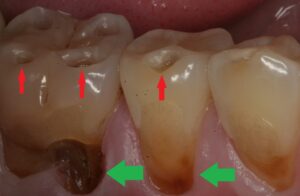
Increased Risk of Decay: A dry mouth creates a more acidic environment, which can accelerate tooth decay and increase the risk of cavities.
2. Gum Disease
Gingivitis and Periodontitis: Lack of saliva can lead to the accumulation of plaque, increasing the risk of gum diseases like gingivitis (inflammation of the gums) and periodontitis (a more severe gum disease that can lead to tooth loss).
3. Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Bacterial Growth: A dry mouth can lead to increased bacterial growth, contributing to bad breath.
4. Tooth Alignment and Jaw Development Issues Malocclusion: Chronic mouth breathing can affect the normal development of the facial and jaw structures, especially in children. This can result in malocclusion (misalignment of teeth), including overbites, underbites, or crossbites.
5.Long Face Syndrome: In children, prolonged mouth breathing can lead to an elongated facial structure, known as “long face syndrome,” which may require orthodontic treatment.
6. Oral Inflammation and Sores
Mouth Ulcers and Sores: The lack of moisture in the mouth can also lead to irritation, sores, and ulcers on the oral mucosa.
Preventive and Corrective Measures
Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups are crucial.
Hydration: Drinking water frequently can help alleviate dry mouth.
Use of Dental Products: Mouthwashes and toothpaste designed for dry mouth can help maintain moisture.
Orthodontic Evaluation: Early orthodontic evaluation can help address potential alignment issues in children.